Redis cache limit
Redis cache limit fault limits the amount of memory used by a Redis cache and restores it after the chaos duration.
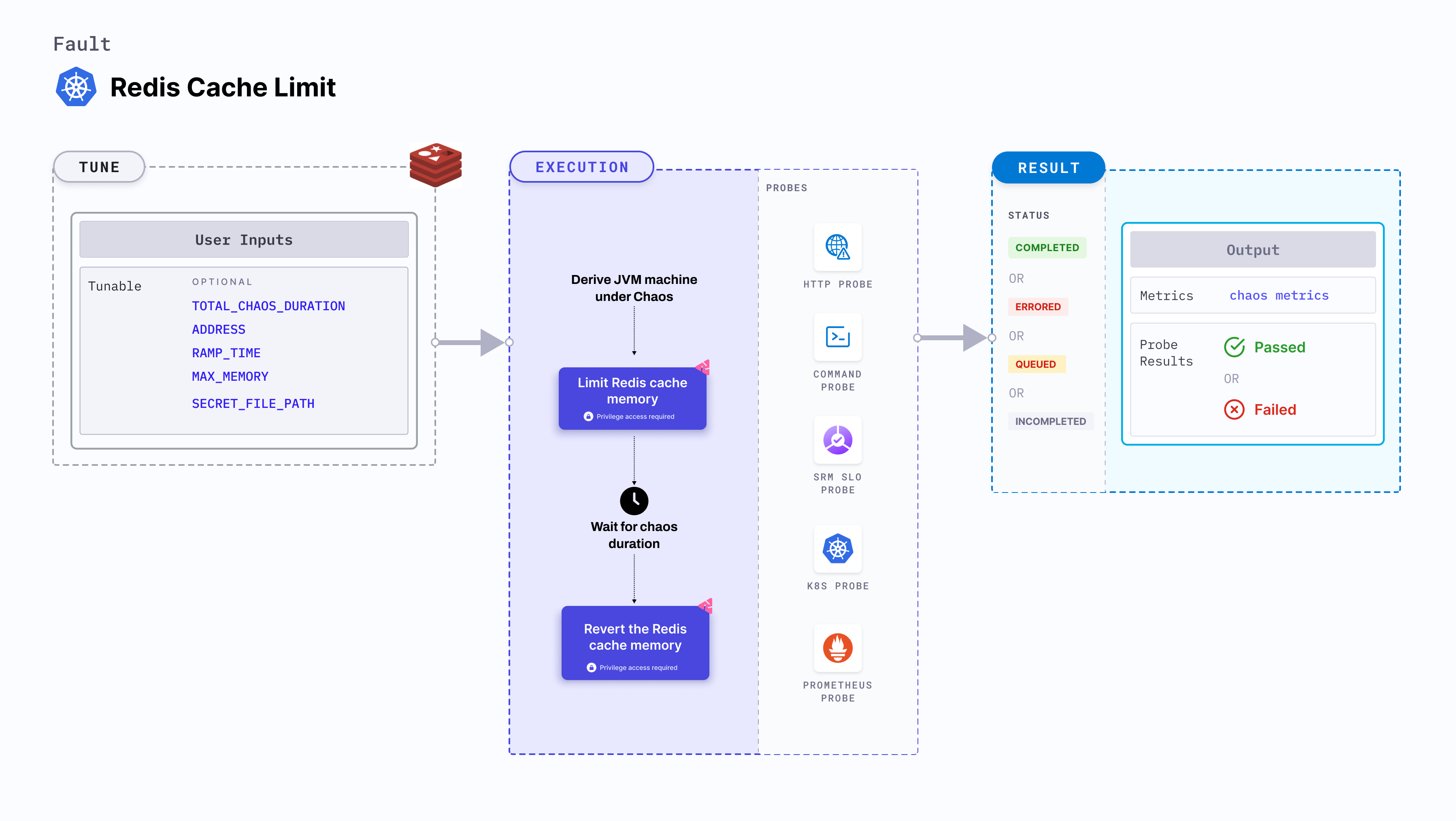
Use cases
Redis cache limit determines the resilience of Redis-dependant applications on frequent cache misses that occur due to a low cache size.
Permissions required
Below is a sample Kubernetes role that defines the permissions required to execute the fault.
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: Role
metadata:
namespace: hce
name: redis-cache-limit
spec:
definition:
scope: Namespaced
permissions:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "patch", "deletecollection", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["events"]
verbs: ["create", "get", "list", "patch", "update"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["pods/log"]
verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["deployments, statefulsets"]
verbs: ["get", "list"]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["jobs"]
verbs: ["create", "delete", "get", "list", "deletecollection"]
Redis authentication
If your Redis server doesn't require authentication, you can directly provide the ADDRESS tunable, that refers to the Redis server address. Refer here.
If your application requires a secret or authentication, provide the ADDRESS, PASSWORD and the TLS authentication certificate. Create a Kubernetes secret (say redis-secret) in the namespace where the fault executes. A sample is shown below.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: redis-secret # Name of the Secret
type: Opaque # Default Secret type
stringData:
redis-secret.yaml: |-
address: 34.136.111.6:6379
password: mypass
tlsCertFile: <cert>
After creating the secret, mount the secret into the experiment, and reference the mounted file path using the SECRET_FILE_PATH environment variable in the experiment manifest. A sample is shown below.
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: K8sFault
metadata:
name: redis-cache-penetration
spec:
definition:
chaos:
env:
... # other env
... # other env
- name: SECRET_FILE_PATH
value: "/tmp/redis-secret.yaml"
components:
secrets: # Kubernetes secret mounted
- name: redis-secret
mountPath: /tmp/
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 30s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s. For more information, go to duration. |
| RAMP_TIME | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos. Should be provided in [numeric-hours]h[numeric-minutes]m[numeric-seconds]s format. | Default: 0s. Examples: 1m25s, 1h3m2s, 1h3s. For more information, go to ramp time. |
| ADDRESS | The address of the Redis server. | If your Redis server doesn't require authentication, directly provide the address. |
| MAX_MEMORY | The percentage of existing Redis maximum memory or an absolute amount (in MB, KB, GB) that should be used by Redis. | Default: 50%. |
| SECRET_FILE_PATH | Path to the file that contains the secret. | If a password or certificate is required alongside the address, use the secret file approach. |
Parameters
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of these tunables:
apiVersion: litmuschaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: KubernetesChaosExperiment
metadata:
name: redis-cache-limit
namespace: hce
spec:
tasks:
- definition:
chaos:
env:
- name: TOTAL_CHAOS_DURATION
value: "60" # in seconds
## Period to wait before and after injection of chaos in sec
- name: RAMP_TIME
value: ""
- name: ADDRESS
value: ""
- name: MAX_MEMORY
value: "50%"
- name: SECRET_FILE_PATH # optional- required only for authentication
value: "/tmp/redis-secret.yaml"